The detrimental effects of smoking on health are well documented, with implications that reach far beyond the commonly discussed respiratory issues. Among these, the impact of smoking on vascular health and specifically lower limb venous insufficiency is significant. This article delves into the intricate relationship between smoking and venous health, exploring how cigarette smoke and its components affect blood circulation, contribute to vascular diseases, and ultimately pose risks to individuals with existing venous conditions. Additionally, we will examine the positive outcomes of quitting smoking and lifestyle changes that can enhance vein health.
What Is the Connection Between Smoking and Venous Insufficiency?
How Does Cigarette Smoke Impact Blood Flow?
Cigarette smoke is a complex mixture of harmful chemicals, including nicotine and carbon monoxide, which adversely affect blood flow in the body. When a person smokes, the nicotine enters the bloodstream, causing blood vessels to constrict, which directly reduces blood flow. This constriction can lead to lower limb venous insufficiency, as the veins in the legs struggle to return blood to the heart efficiently. Moreover, smoking decreases the oxygen levels in the blood, thereby impairing the function of blood cells and the overall delivery of nutrients to tissues. As a result, the legs may experience symptoms such as swelling and fatigue, indicating compromised venous health.
What Are the Effects of Nicotine on Vein Health?
Nicotine, a primary component of tobacco, has several detrimental effects on vein health. It not only causes vasoconstriction but also promotes inflammation within the blood vessel walls. This inflammation can lead to the development of venous disease, as the blood vessels become increasingly damaged over time. In addition, nicotine has been shown to interfere with the normal functioning of endothelial cells, which line the blood vessels. This dysfunction can result in the increased risk of blood clots, further exacerbating venous insufficiency. The cumulative effects of nicotine make it a significant risk factor for individuals susceptible to vascular issues.
Can Smoking Lead to Peripheral Artery Disease?
Yes, smoking is a well-established risk factor for peripheral artery disease (PAD), a condition characterized by narrowed arteries that reduce blood flow to the limbs. Studies indicate that smokers are much more likely to develop PAD than non-smokers. The mechanisms at play include the promotion of atherosclerosis, where plaque builds up in the arteries, leading to reduced blood circulation. This condition not only affects the arteries but can also have cascading effects on the veins, contributing to lower limb venous insufficiency. Thus, smoking can indeed precipitate a cycle of vascular complications that impact overall health.
How Does Smoking Affect Varicose Veins and Overall Vascular Health?
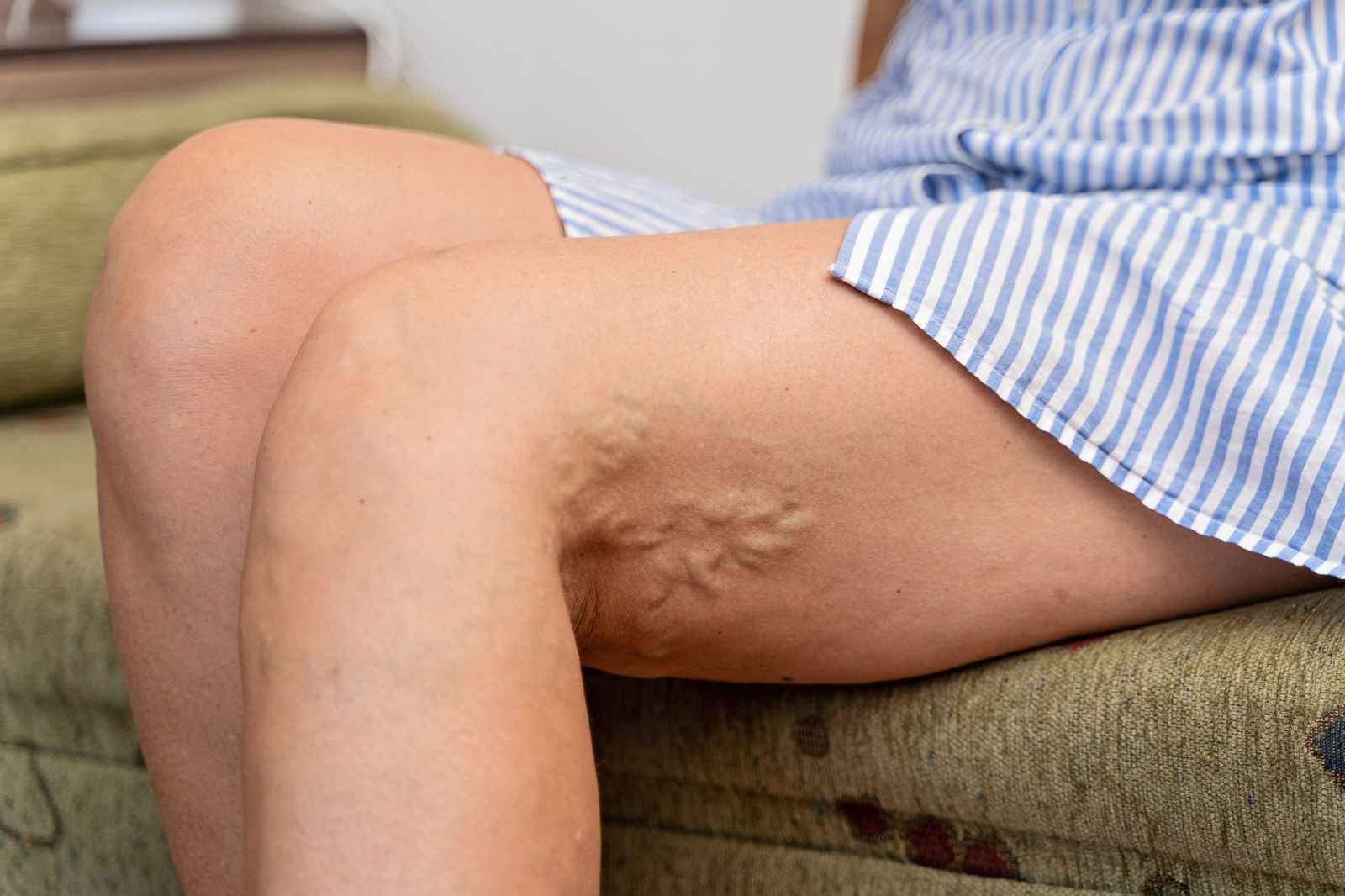
What Are Varicose Veins and Their Causes?
Varicose veins are enlarged, twisted veins that often appear blue or dark purple and can be seen just beneath the skin’s surface. They occur when the valves within the veins weaken or fail, causing blood to pool in the veins rather than flow efficiently back to the heart. Several factors contribute to the development of varicose veins, including genetics, age, and lifestyle choices, with smoking being a notable risk factor. The harmful substances in tobacco can weaken vein walls and compromise valve function, thereby increasing the likelihood of developing varicose veins.
How Does Tobacco Smoking Contribute to Vascular Disease?
Tobacco smoking contributes to vascular disease in multiple ways. The chemicals in cigarette smoke, including carbon monoxide, can damage endothelial cells and promote inflammation throughout the vascular system. This damage can lead to the thickening of blood vessel walls, known as vascular remodeling, which compromises the vessels’ ability to transport blood effectively. Smoking also increases the risk of blood clots, which can lead to serious conditions such as deep vein thrombosis (DVT) and pulmonary embolism, further complicating venous health. The cumulative effects of tobacco smoking create a precarious environment for vascular integrity, leading to a range of health complications.
What Role Does Smoking Play in Blood Vessel Damage?
Smoking plays a critical role in blood vessel damage through the introduction of toxic substances that compromise vascular integrity. The exposure to cigarette smoke leads to oxidative stress, which damages the cells lining the blood vessels. Over time, this can result in chronic inflammation and vascular remodeling, ultimately contributing to the development of conditions such as venous insufficiency. Furthermore, the presence of nicotine can disrupt the balance of nitric oxide, a molecule that helps maintain vascular health by promoting vasodilation. Disruption of this balance can lead to significant impairments in circulation, exacerbating existing venous issues.
What Are the Risks of Smoking for People with Existing Venous Issues?
How Does Smoking Increase the Risk of Venous Insufficiency?
For individuals already experiencing venous issues, smoking significantly increases the risk of worsening symptoms and complications. The harmful effects of smoking can exacerbate the underlying conditions that lead to venous insufficiency, such as valve dysfunction and venous hypertension. Additionally, smoking can lead to poor circulation, which further complicates existing venous problems. The combination of impaired blood flow and increased venous pressure can result in severe symptoms, including pain, swelling, and skin changes. Therefore, smoking poses a serious threat to those already suffering from venous diseases.
Are Smokers More Likely to Experience Poor Circulation?
Yes, smokers are more likely to experience poor circulation compared to non-smokers. The constrictive effects of nicotine and the damage caused by other harmful chemicals in cigarette smoke can reduce overall blood flow, leading to symptoms such as cold extremities, numbness, and cramping. Poor circulation can also contribute to the development of more severe conditions, such as peripheral artery disease and chronic venous insufficiency. As a result, smokers not only face the immediate risks associated with smoking but also long-term consequences that can significantly impact their vascular health.
What Are the Cardiovascular Implications of Smoking?
The cardiovascular implications of smoking are profound and multifaceted. Smoking contributes to the development of atherosclerosis, increasing the risk of heart attack and stroke. Additionally, it can lead to elevated blood pressure and increased heart rate, further straining the cardiovascular system. For those with pre-existing conditions such as diabetes or high cholesterol, smoking compounds these risk factors, heightening the likelihood of severe cardiovascular events. Overall, smoking poses a significant threat to heart health, making it imperative for individuals to recognize the importance of quitting smoking to safeguard their vascular health.
How Can Quitting Smoking Improve Vein Health?
What Are the Benefits of Stopping Smoking for Your Veins?
Quitting smoking can have immediate and long-term benefits for vein health. Within days of stopping smoking, circulation begins to improve as blood flow increases and blood vessel function begins to normalize. Over time, the risk of developing vascular diseases decreases significantly, and existing conditions such as varicose veins may improve as inflammation and oxidative stress diminish. Furthermore, quitting smoking can enhance the effectiveness of treatments for venous issues, allowing individuals to experience better outcomes in managing their conditions. The decision to stop smoking is a powerful step toward achieving better vein health.
How Long Does It Take for Vein Health to Improve After Quitting?
The timeline for improvement in vein health after quitting smoking can vary among individuals, but many can expect to see significant changes within weeks to months. Initial improvements in circulation can occur within a few days, while more substantial benefits, such as reduced risk of venous disease and improved vein function, may take several months to manifest. Studies have shown that individuals who quit smoking experience a gradual decrease in the prevalence of symptoms associated with venous insufficiency over time. Sustained abstinence from smoking can lead to marked improvements in overall vascular health.
What Resources Are Available to Help You Quit Smoking?
Numerous resources are available to assist individuals in their journey to quit smoking. Support options include counseling services, helplines, and smoking cessation programs, which provide guidance and support based on evidence-based practices. Additionally, pharmacological aids such as nicotine replacement therapies and prescription medications can help manage withdrawal symptoms and cravings. Online resources, including websites dedicated to smoking cessation, offer valuable information and community support. For those seeking to quit smoking, leveraging these resources can significantly enhance the chances of success and promote improved vein health.
What Lifestyle Changes Can Support Vein Health Apart from Quitting Smoking?
How Does Diet Affect Venous Insufficiency?
Diet plays a crucial role in supporting vein health and managing venous insufficiency. A balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins can help maintain a healthy weight and reduce the strain on the venous system. Foods high in fiber can prevent constipation, which can exacerbate venous issues. Moreover, consuming anti-inflammatory foods, such as fatty fish and nuts, can help reduce inflammation in the blood vessels. It’s also important to limit salt intake to prevent fluid retention, which can worsen symptoms of venous insufficiency.
What Exercises Can Improve Blood Flow in the Limbs?
Regular physical activity is essential for improving blood flow in the limbs and supporting overall vascular health. Exercises such as walking, cycling, and swimming promote circulation by engaging the muscles and encouraging venous return. Additionally, leg exercises that involve calf raises and ankle pumps can help prevent blood from pooling in the lower extremities. Incorporating stretching and flexibility exercises into a routine can also enhance overall vascular function. By maintaining an active lifestyle, individuals can significantly improve blood flow and alleviate symptoms associated with venous insufficiency.
How Does Managing Diabetes and Cholesterol Impact Vein Health?
Managing diabetes and cholesterol is vital for maintaining vein health and reducing the risk of venous issues. Elevated blood sugar levels can damage blood vessels, while high cholesterol can lead to the buildup of plaque within arteries, both of which can compromise circulation. Individuals with diabetes should maintain their blood sugar levels within target ranges through diet, exercise, and medications as needed. Additionally, monitoring cholesterol levels and adhering to a heart-healthy diet can help reduce the risk of vascular disease. By actively managing these health factors, individuals can enhance their vein health and reduce the risk of complications associated with smoking.
Quitting smoking is one of the most effective steps individuals can take to improve their vein health and overall vascular well-being. The harmful effects of smoking on circulation, vein function, and cardiovascular health are well-documented, but the good news is that the body has an incredible ability to heal. By embracing a smoke-free lifestyle, adopting healthy habits such as regular exercise and a balanced diet, and seeking medical guidance when needed, individuals can significantly reduce their risk of venous insufficiency and other vascular diseases. Prioritizing vein health is not just about aesthetics—it’s about ensuring long-term mobility, comfort, and overall quality of life.




Leave A Comment